Using the LM35 temperature sensor in the BeagleBone Black
In this post, I show how to read the temperature from the analog sensor LM35. The datasheet can be found here. This sensor has an output voltage linearly-proportional to the Centigrade temperature of 10mV/°C and, it can measure in a range of -55°C - 150°C attaching a resistor from the output pin to a negative source voltage, but it is common used to using it in a temperature range from 2° to 150°C, due that, the resistor is not necessary.
It is important to remember that the BeagleBone has 7 analog inputs and ADC of 12 bits that let to de user to represent an analog signal within a range of 4096 values. It is important to remember that the reference for analog voltage is 1.8V. If the user provides a greater voltage, the BeagleBone could be damaged.
Keeping this in mind, at 150°C this sensor will produce an output voltage of 1.5V, which is inside the range of the ADC. For reference, in this post, I showed how to use the ADC module in the BeagleBone.
Circuit and components
The circuit can be seen in Figure 1. It consists of an LM35 and the BeagleBone.
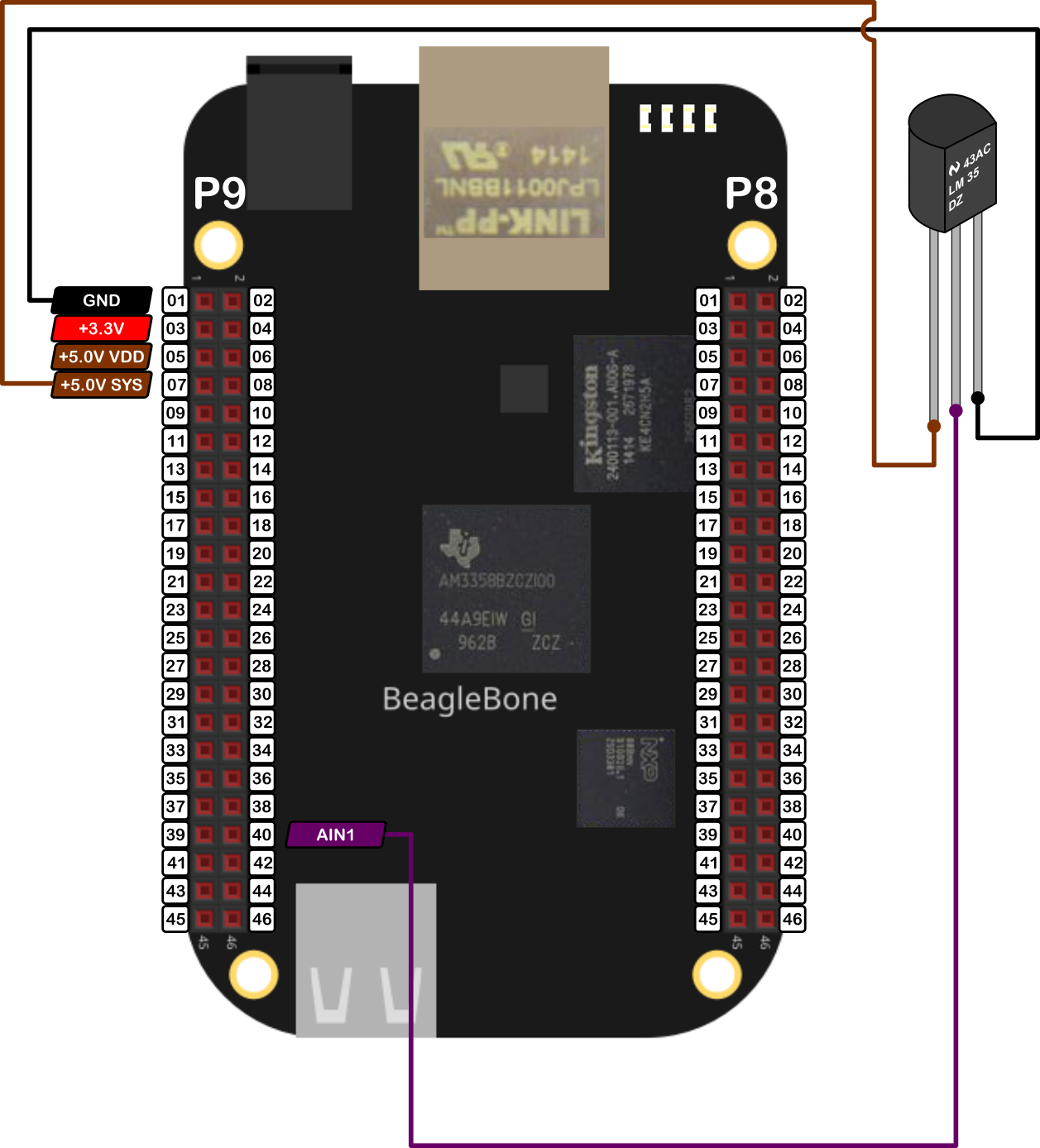
The components are:
- 1 LM35
- Jumpers male-male to make the connections
Coding
An LM35 object is declared with global scope to initialize the sensor from which the LM35 sensor will be attached to.
1
2
// Global ADC pin declaration
LM35 mySensor(P9_40);
Three global variables are defined and initialized to stop the reading process and store the temperature in °C and °F.
1
2
3
4
// Global Variables
bool stopReadTemperature = false;
double temperatureCelsius = 0.0;
double temperatureFahrenheit = 0.0;
A callback function is used to measure in background the temperature while a bool variable is false.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
int ReadTemperature() {
while (stopReadTemperature == false)
{
temperatureCelsius = mySensor.ReadTemperatureCelsius();
temperatureFahrenheit = mySensor.ReadTemperatureFahrenheit();
cout << "'y' for exit" << endl;
Delayms(250);
}
return 0;
}
The methods to get the temperature are ReadTemperatureCelsius() and ReadTemperatureFahrenheit() which get the data from the sensor and return the read value stored in a private member of the class LM35.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/*
Public method to get the temperature in °C
@return double: the measured temperature (2°C - 150°C)
*/
double LM35::ReadTemperatureCelsius()
{
// Get the reading
this->ReadDataFromSensor();
std::string message;
message = "Temperature: " + std::to_string(temperatureCelsius) + " °C\n";
std::cout << RainbowText(message, "Neon Green");
return temperatureCelsius;
}
/*
Public method to get the temperature in °F
@return double: the measured temperature (35.6°F - 302°F)
*/
double LM35::ReadTemperatureFahrenheit()
{
// Get the reading
this->ReadDataFromSensor();
std::string message;
message = "Temperature: " + std::to_string(temperatureFahrenheit) + " °F\n";
std::cout << RainbowText(message, "Neon Green");
return temperatureFahrenheit;
}
The core method used to get the data from the sensor is ReadDataFromSensor() which interacts with the ADC pin directly reading the voltage, mapping it to a °C and °F and, finally store these values in private variables which can be accessed by the ReadTemperatureCelsius() and ReadTemperatureFahrenheit() methods.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/*
Private method to read and store the data from the sensor
*/
void LM35::ReadDataFromSensor()
{
double voltageFromSensor = ADCPin.ReadVoltage();
temperatureCelsius = voltageFromSensor * 100;
temperatureFahrenheit = temperatureCelsius * 1.8 + 32;
}
The complete code for this implementation is shown in the next listing:
LM35_1.1.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
/******************************************************************************
LM35_1.1.cpp
@wgaonar
05/08/2021
https://github.com/wgaonar/BeagleCPP
Read the temperature each 250 ms until the user enter a keystroke
Class: LM35
******************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include "../../../Sources/LM35.h"
using namespace std;
// Global ADC pin declaration
LM35 mySensor(P9_40);
// Global Variables
bool stopReadTemperature = false;
double temperatureCelsius = 0.0;
double temperatureFahrenheit = 0.0;
int ReadTemperature() {
while (stopReadTemperature == false)
{
temperatureCelsius = mySensor.ReadTemperatureCelsius();
temperatureFahrenheit = mySensor.ReadTemperatureFahrenheit();
cout << "'y' for exit" << endl;
Delayms(250);
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
string message = "Main program starting here...";
cout << RainbowText(message,"Blue", "White", "Bold") << endl;
// Call the function to read the temperature
mySensor.DoUserFunction(&ReadTemperature);
char userInput = '\0';
while (userInput != 'y')
{
message = "Do you want to stop the readings on the pin? Enter 'y' for yes: ";
cout << RainbowText(message, "Blue") << endl;
cin >> userInput;
if (userInput == 'y')
stopReadTemperature = true;
}
message = "Main program finishes here...";
cout << RainbowText(message,"Blue", "White","Bold") << endl;
return 0;
}
Execution of the program:
Se you in the next post.