Reading an analog value from a potentiometer in the BeagleBone Black
In this post, I show a simple application of the analog to digital converter (ADC) C++ class implementation shown previously in this post. Remembering that the BeagleBone has 7 analog inputs and ADC of 12 bits that let to de user to represent an analog signal within a range of 4096 values. It is important to remember that the reference for analog voltage is 1.8V. If the user provides a greater voltage, the BeagleBone could be damaged.
Circuit and components
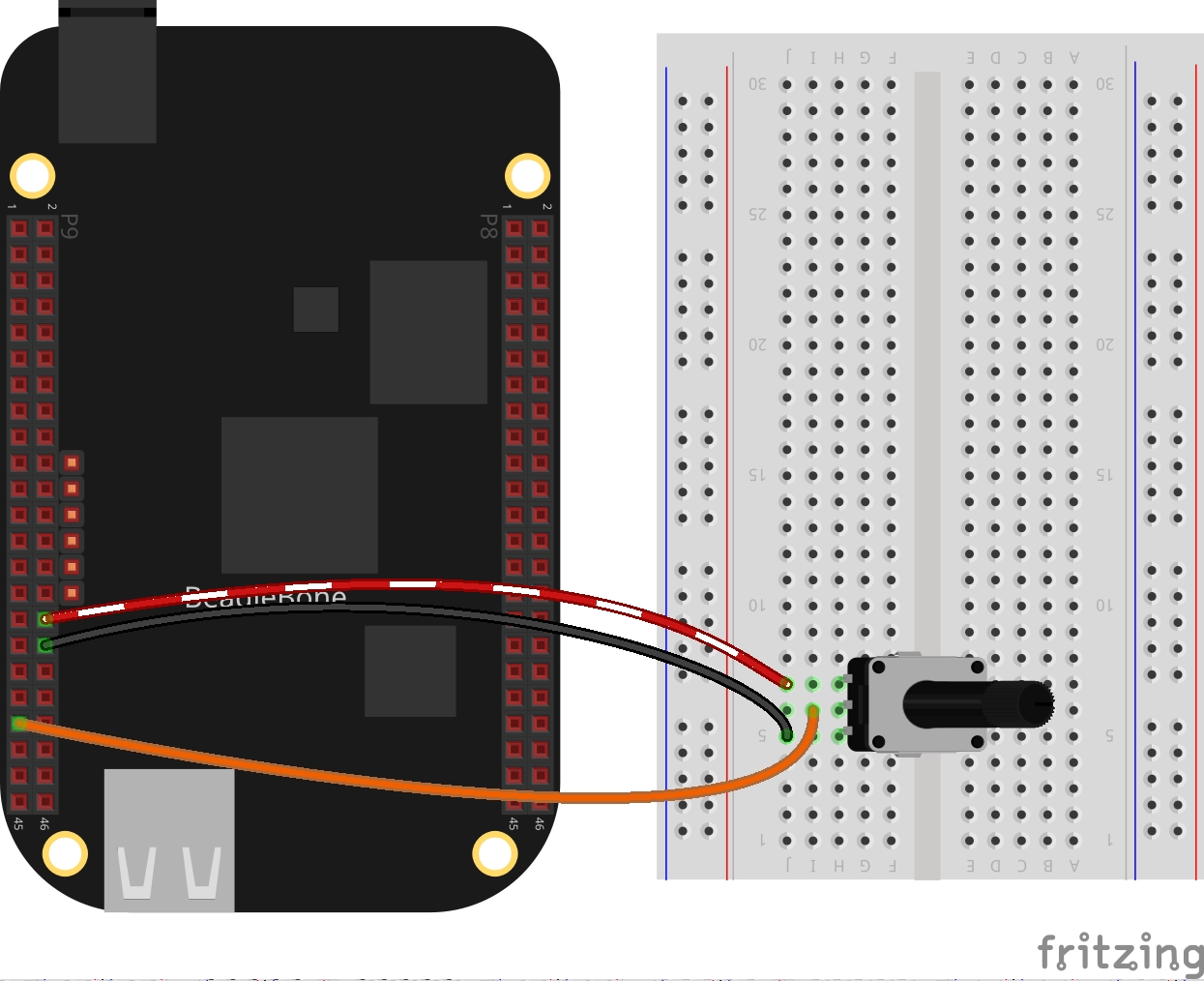
The circuit can be seen in Figure 1. It consists of a Potentiometer with a power supplied using the analog ground pin 0V located at the pin P9_34 and to analog VDD pin at 1.8V located at the pin P9_32. Finally, its output is connected to the P9_39 pin.
The components are:
- 1 Potentiometer of 200KΩ
- Jumpers male-male to make the connections
Coding
First an ADC class object is declared, for example:
1
ADC adcPin(P9_39);
An integer variable is declared and initialized to store the digital converted values.
1
2
int adcValue = 0;
The digital values can be obtained through the next class method:
1
adcValue = adcPin.ReadADC();
Now, this method can be inside of a for loop to take 100 readings for example every 100 milliseconds:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
adcValue = adcPin.ReadADC();
cout << "Reading " << i+1 << " of " << " 100: ";
cout << adcValue << endl;
adcPin.Delayms(100);
}
The complete code for this application is shown in the next listing together with its corresponding execution video.
Listing_5.1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
#include <iostream>
#include "../../Sources/ADC.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string message = "Main program starting here...";
cout << RainbowText(message,"Blue", "White", "Bold") << endl;
message = "Setting ADC mode on a pin";
cout << RainbowText(message, "Blue") << endl;
ADC adcPin(P9_39);
message = "Read an analog value and wait 100 milliseconds between each read";
cout << RainbowText(message, "Blue") << endl;
int adcValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
adcValue = adcPin.ReadADC();
cout << "Reading " << i+1 << " of " << " 100: ";
cout << adcValue << endl;
adcPin.Delayms(100);
}
message = "Main program finishes here...";
cout << RainbowText(message,"Blue", "White","Bold") << endl;
return 0;
}
Execution of the program:
Se you in the next post.